Exploring the Differences Between Always On Availability Groups and Distributed Availability Groups (DAGs) in SQL Server
A distributed availability
group (AG) is a special type of availability group that spans two separate
availability groups. Distributed availability groups are available starting
with SQL Server 2016.
The availability groups that participate in a distributed availability group don't need to be in the same location. They can be physical, virtual, on-premises, in the public cloud, or anywhere that supports an availability group deployment.
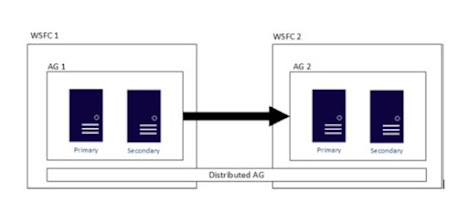
The following figure shows a high-level
view of a distributed availability group that spans two availability groups (AG
1 and AG 2), each configured on its own WSFC. The distributed availability
group has a total of four replicas, with two in each availability group. Each
availability group can support up to the maximum number of replicas, so a
distributed availability can have up to 18 total replicas.
However, data movement is
slightly different within distributed availability groups compared to a
traditional availability group. Although each availability group has
a primary replica, there is
only one copy of the databases participating in a distributed availability
group that can accept inserts, updates, and deletions.
As shown in the following figure, AG 1 is
the primary availability group. Its primary replica sends transactions to both
the secondary replicas of AG 1 and the primary replica of AG 2. The primary
replica of AG 2 is also known as a forwarder. A forwarder is a
primary replica in a secondary availability group in a distributed availability
group. The forwarder receives transactions from the primary replica in the
primary availability group and forwards them to the secondary replicas in its
own availability
The only way to make AG 2's primary replica
accept inserts, updates, and deletions, is to manually fail over the
distributed availability group from AG 1. In the preceding figure, because AG 1
contains the writeable copy of the database, issuing a failover makes AG 2 the
availability group that can handle inserts, updates, and deletions.

Comments
Post a Comment